Associate Professor Yang Liu (PhD supervisor) from the College of Information and Intelligent Science at Donghua University has recently made notable progress in the study of morphological characteristics and optical asymmetry in chiral gold nanorod (Au-NR) helical assemblies. The team achieved data-driven “structure–property” correlation modeling and inverse structural design. The related research outcomes have been published in Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence and Materials & Design.
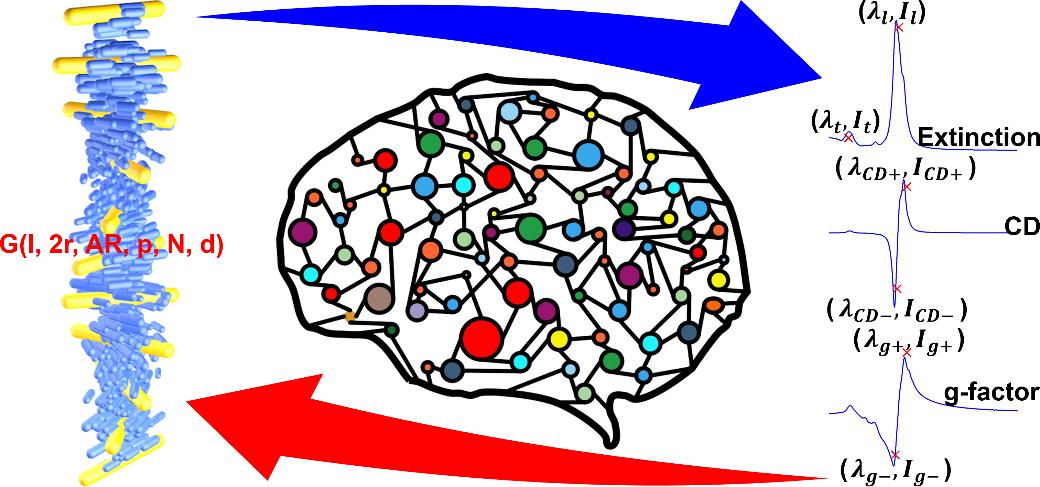
Figure 1. Research schematic diagram
In earlier work, Prof. Liu successfully constructed Au-NR helical assemblies within cholesteric liquid crystals (CLCs), demonstrating photo-responsive and asymmetrically tunable chiral optical properties (Adv. Optical Mater. 2024, 2400862). As the work advanced, he came to recognize that the ability to efficiently predict the structure–propertyrelationships of these microstructures would play a key role in directing and optimizing subsequent experimental research. Under Prof. Liu’s supervision, postgraduate students Chen Yongguang, Yang Bo, and others independently built a specialized dataset using Finite-Difference Time-Domain (FDTD) simulations. They systematically investigated the intrinsic correlations between the geometric parameters of Au-NR helices and optical asymmetry indicators, including extinction spectra, circular dichroism (CD) spectra, and the g-factor. An artificial neural network (ANN) framework was then developed to predict optical asymmetry, along with a Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO)-based inverse design workflow for retrieving geometric configurations corresponding to target optical responses.
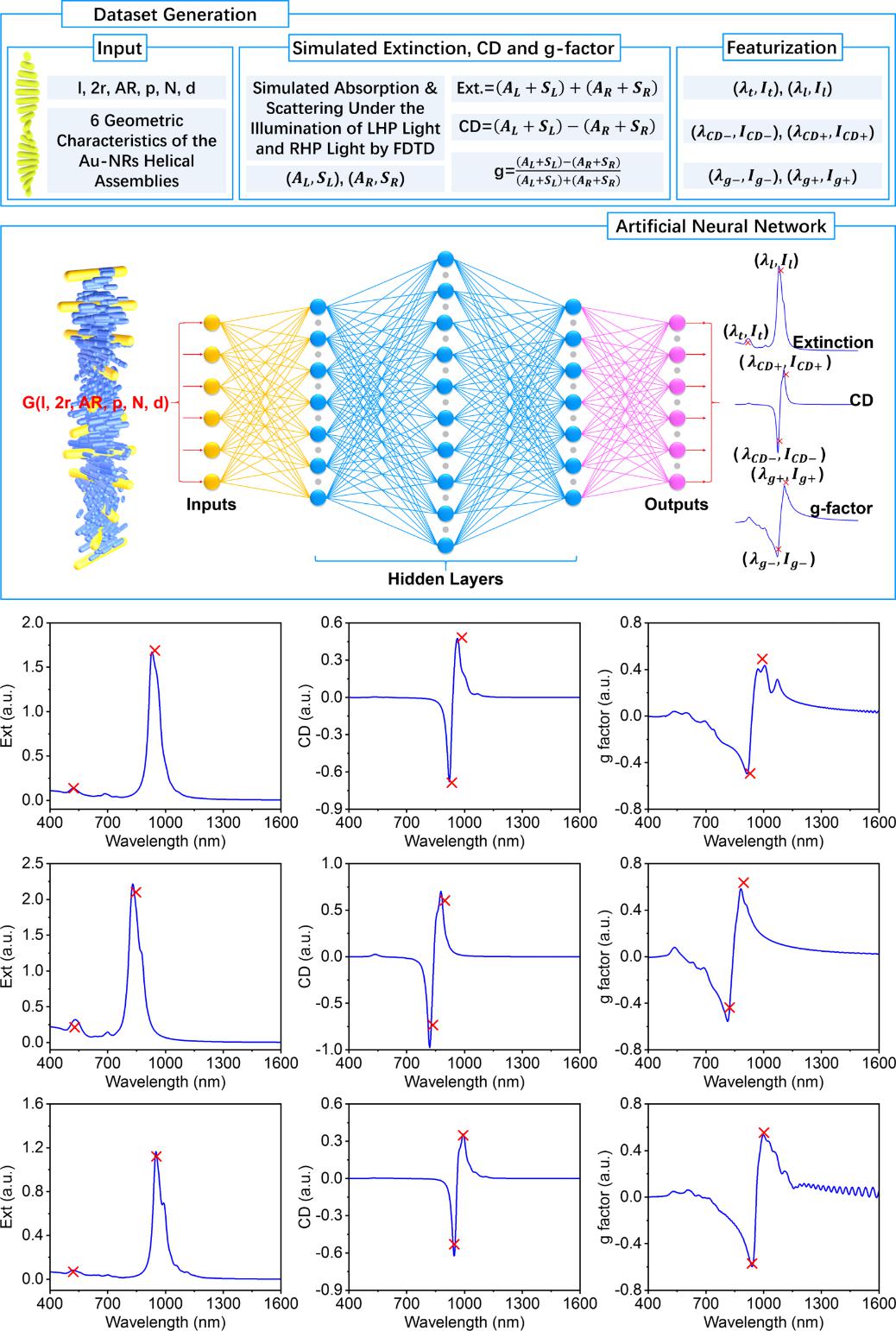
Figure 2. Schematic of the 3NHL50NN for predicting optical asymmetry of Au-NRs helical assemblies and its prediction results
The designed ANN model (3NHL50NN) demonstrated excellent predictive performance, achieving a coefficient of determination R² > 0.998 across multiple target parameters. Moreover, the model improved computational efficiency by over 99.99% (Figure 2), reducing prediction time from hours (required by traditional FDTD methods) to milliseconds, enabling rapid and scalable microstructure optical analysis.
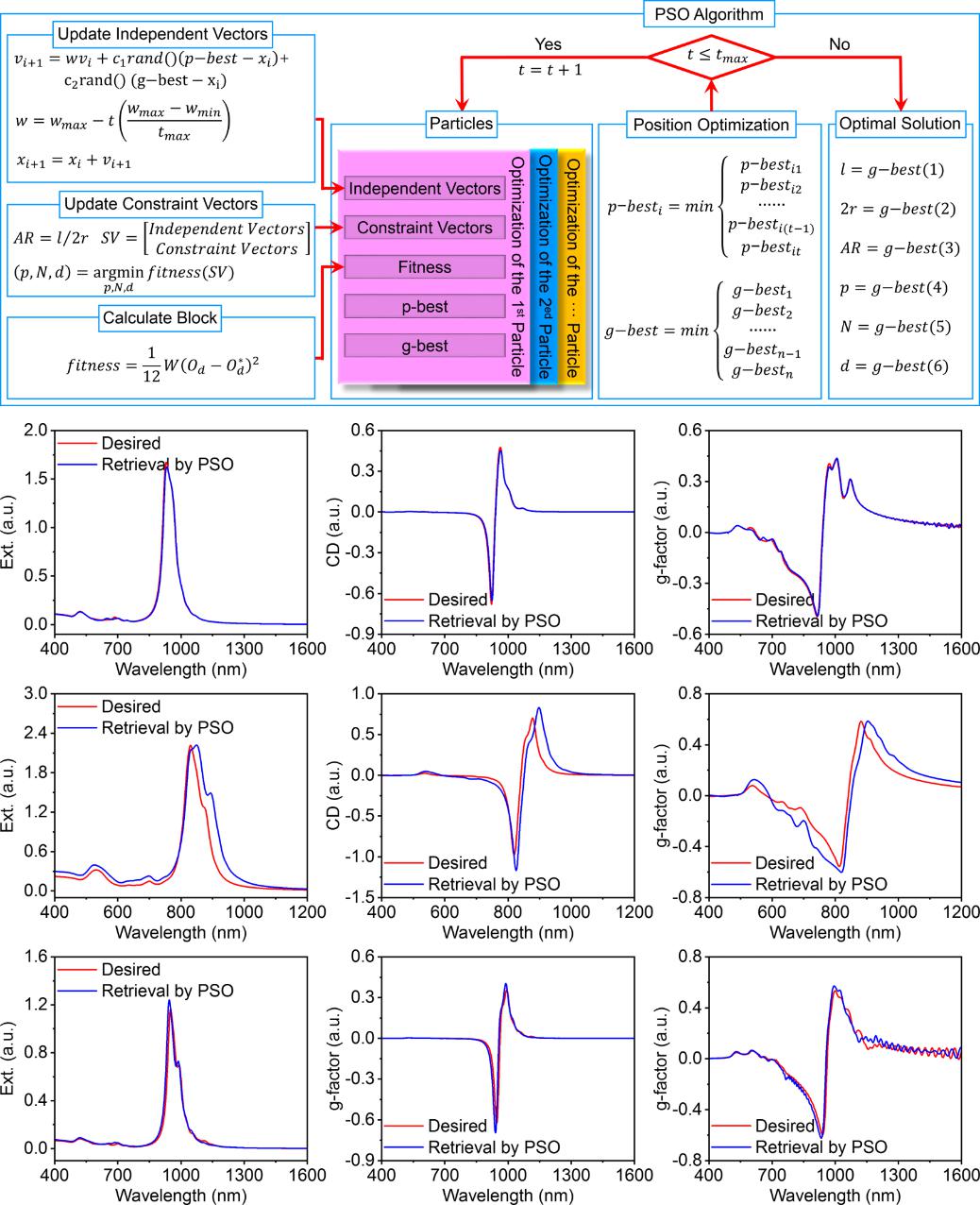
Figure 3. Schematic of the PSO algorithm for retrieving geometric characteristics of Au-NRs helical assemblies, and comparison between simulation results and theoretical expectations
To address the challenge of inverse design for Au-NR helical assemblies, the team innovatively integrated the prediction network with the PSO algorithm. By employing the overlap coefficient between the target and predicted spectra as the fitness function, and introducing a linearly decreasing inertia weight strategy, the method effectively balances global exploration and local optimization. This enables rapid and accurate retrieval of geometric parameters from desired optical responses. Remarkably, the algorithm outputs geometric configurations matching the target optical asymmetry in as little as 6 seconds, demonstrating both high precision and computational efficiency. The Au-NR helical assemblies fabricated based on the retrieved parameters showed optical behaviors that closely aligned with theoretical predictions (Figure 3). These findings confirm that the team has not only achieved accurate prediction of optical asymmetry in such microstructures, but also established a reliable capability for inverse deduction of geometry from optical data.
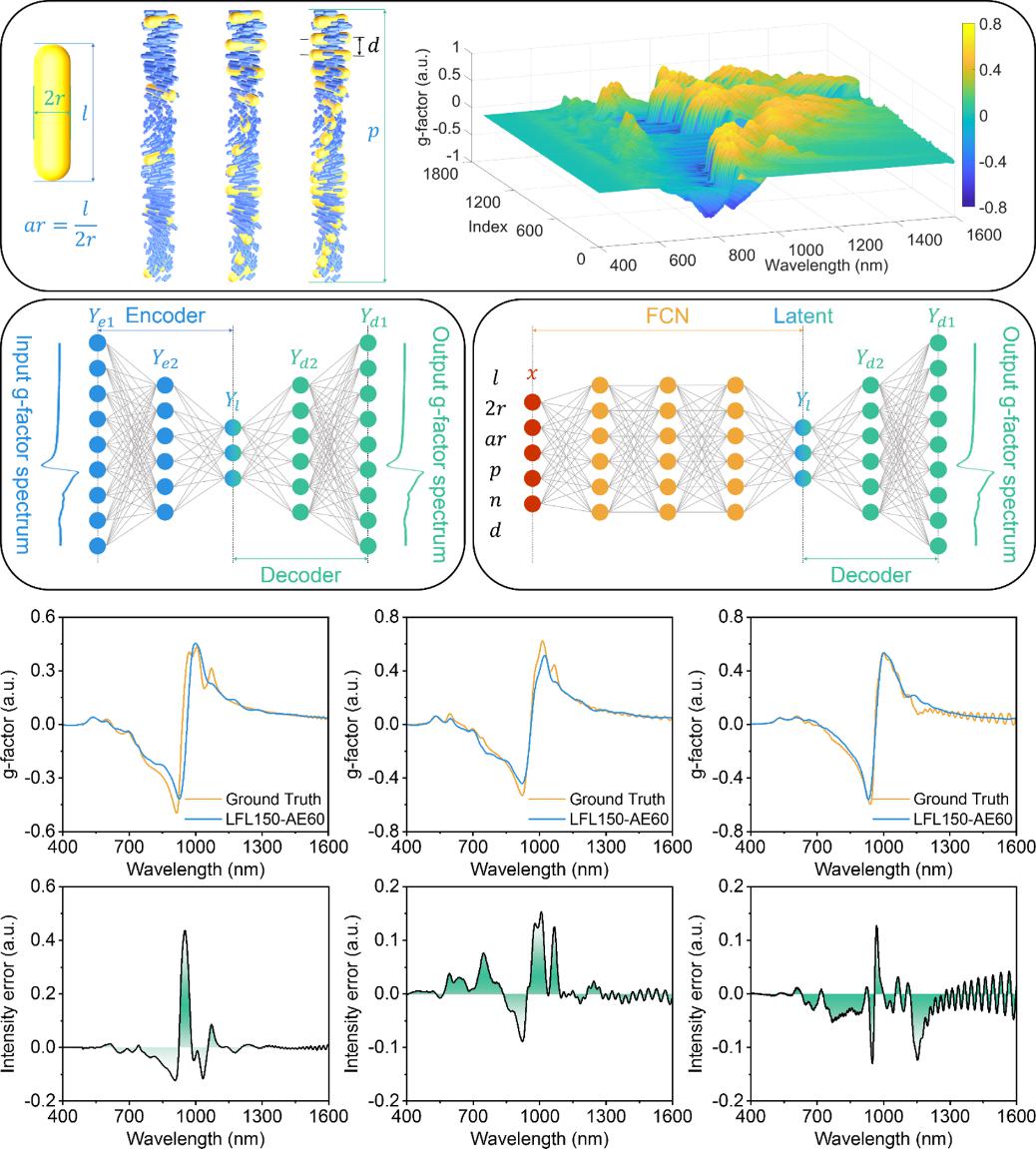
Figure 4. Schematic of the LFL150-AE60 network predicting g-factor spectra, and the deviation between its predictions and FDTD simulation results
The team further optimized the ANN architecture to form the LFL150-AE60 network, enabling high-precision prediction of g-factor spectra over a broad 400–1600 nm wavelength range, achieving a correlation coefficient of 0.983 (Figure 4). Its prediction speed is eight orders of magnitude faster than conventional FDTD simulations, providing a powerful computational tool for optical design and regulation.
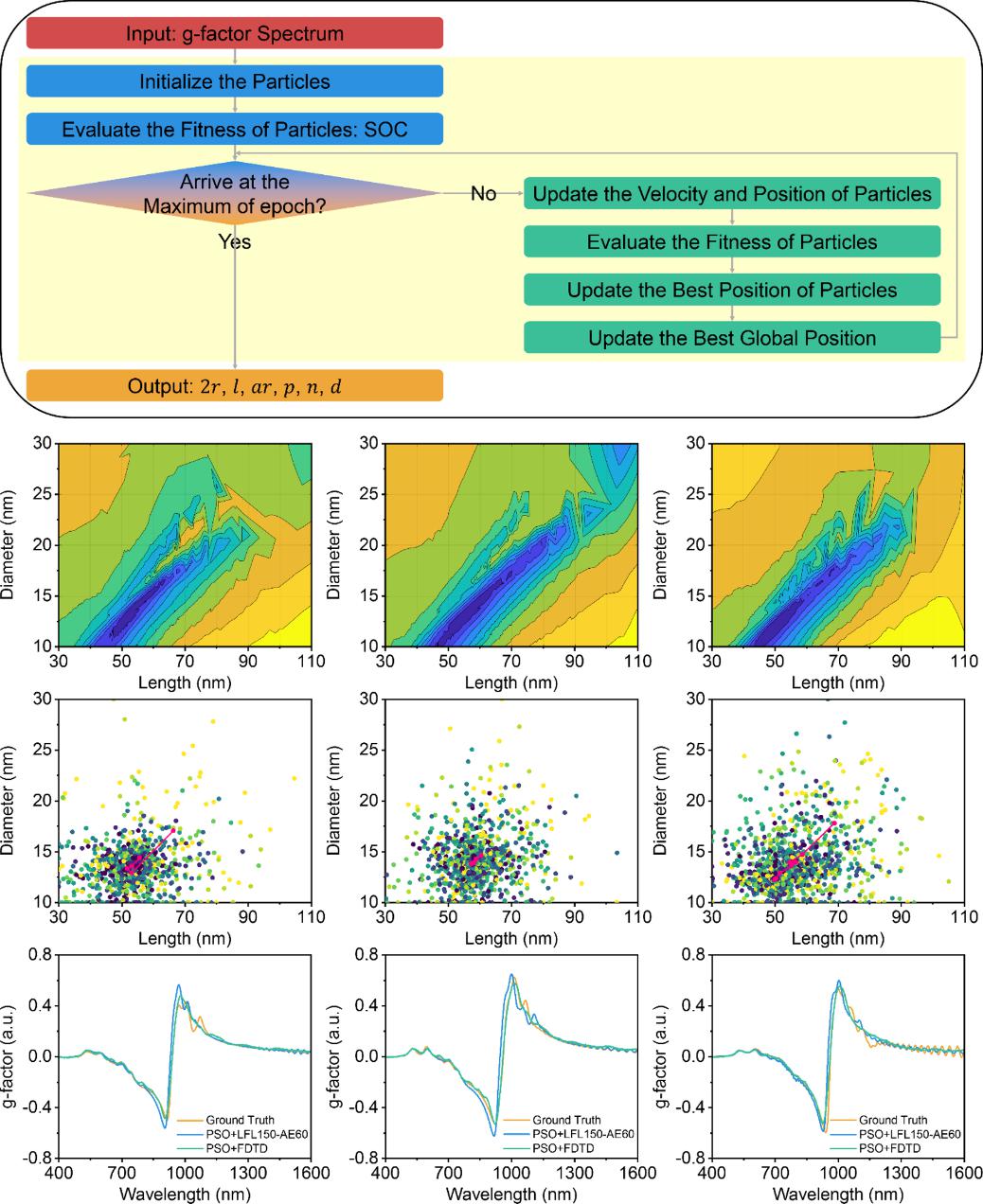
Figure 5. Schematic of the PSO algorithm optimized by integrating the LFL150-AE60 network, and its search trajectory and result comparison during the inversion process
Prof. Liu’s team further integrated the LFL150-AE60 network with the particle swarm algorithm to optimize the PSO-based inverse design workflow for retrieving the geometric characteristics of Au-NR helical assemblies (Figure 5). The upgraded PSO–LFL150-AE60 algorithm significantly enhances usability, requiring only the target g-factor spectrum as input to directly obtain the corresponding geometric parameters. The reconstructed g-factor spectra based on the retrieved parameters exhibited excellent agreement with the target spectra, demonstrating high accuracy and reliability. This advancement further highlights the strength of the PSO–LFL150-AE60 approach in the inverse design of microstructures and provides a reliable method for the precise structural design of systems exhibiting optical asymmetry.
The research was led by Prof. Liu Yang. Main contributions were made by Chen Yongguang (M.Sc. 2023, Control Science and Engineering), Wei Xiyang (M.Sc. 2023, Information and Communication Engineering), and Yang Bo (M.Sc. 2024, Electronic Information). Associate Professor Shang Jianhua (DHU) and Assistant Professor Zhao Lina (City University of Hong Kong) also provided important support. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai, the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, and the Hong Kong Research Grants Council (RGC).
Related Publications
Liu Yang*, Chen Yongguang, Wei Xiyang, Shang Jianhua, Zhao Lina*. Uncovering the Geometry-Dependent Optical Asymmetry of Gold Nanorod Helical Assemblies Using Artificial Neural Networks. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence 162, 112513 (2025). (CAS Q1, Top)
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0952197625025448
Liu Yang*, Chen Yongguang, Yang Bo, Zhao Lina*. Data-Driven Prediction and Inverse Design of Optical Asymmetry in Gold Nanorod-Helical Assemblies. Materials & Design 259, 114788 (2025). (CAS Q2)
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0264127525012080


